Abstract
This survey provides an in-depth analysis of the recent advancements and applications of Threat Intelligence in Software-Defined Networking (SDN) for enhancing cloud computing and its security. It encompasses a range of studies conducted between 2020 and 2024, highlighting the evolving methodologies, results, and potential drawbacks. The paper aims to present a comprehensive overview of the current state and future prospects of integrating threat intelligence in SDN to safeguard cloud environments.
Table Of Contents
1.1.Software-Defined Networking (SDN). 4
1.2.Software-Defined Networking Security. 5
1.5.Threat Intelligence for SDN Security and its impact on cloud computing. 7
1.5.1.Threat Intelligence in SDN Security. 7
1.5.2.Impact on Cloud Computing. 7
2.1. Historical Evolution of Threat Intelligence in SDN.. 9
2.2. Theoretical Frameworks and Models in SDN-Based Threat Intelligence. 9
2.3. Case Studies on Threat Intelligence Implementation in SDN.. 10
2.4. Technologies and Tools in SDN for Threat Intelligence. 10
2.5. Methodologies for Threat Detection and Response in SDN.. 11
2.6. Integration Challenges and Solutions. 11
2.7. Performance Metrics and Evaluation of SDN-Based Threat Intelligence Systems. 12
2.8.Impact of SDN-Based Threat Intelligence on Cloud Security. 13
2.9. Future Trends and Emerging Research in SDN and Threat Intelligence. 13
03. How The Threat Intelligence for SDN Security Impacted for Cloud Computing. 15
3.1. Foundations of Software-Defined Networking (SDN) in Cloud Computing. 15
3.2. Role and Importance of Threat Intelligence in Cloud Security. 15
3.3. Integrating Threat Intelligence into SDN for Enhanced Cloud Security. 15
3.4. Tools and Technologies in SDN-Based Threat Intelligence for Cloud Security. 16
3.5. Methodological Approaches to Threat Detection and Prevention in SDN-Enabled Cloud Systems. 16
3.6. Challenges and Limitations in Implementing Threat Intelligence in SDN for Cloud Computing. 16
3.7. Case Studies and Real-World Applications. 16
3.8. Impact of Threat Intelligence on Cloud Computing Security and Performance. 16
3.9. Emerging Trends and Future Directions in SDN and Cloud Security. 16
3.10. Critical Analysis and Synthesis of Reviewed Literature. 17
01. Introduction
Software-Defined Networking has emerged as a transformative technology in cloud computing, introducing flexibility and control over network resources. With the rise in cyber threats, integrating Threat Intelligence into SDN has become crucial. This survey explores the evolution of this integration, focusing on how it enhances security measures in cloud computing and addresses emerging cyber threats which can be prevented through threat intelligence.
1.1.Software-Defined Networking (SDN)
is an innovative approach to network management that seeks to improve network flexibility and performance. Unlike traditional network architectures where the control and data planes are integrated into network hardware (like switches and routers), SDN separates the network’s control logic (control plane) from the underlying routers and switches that forward traffic (data plane). This separation allows network administrators to manage network services through abstraction of lower-level functionality.
Key aspects of SDN include.
- Centralized Network Control
By decoupling the control and data planes, SDN allows network administrators to centrally manage and control network traffic with software applications, providing a bird’s-eye view of the entire network.
- Programmability
Networks can be programmed and managed more like software applications, rather than through hardware. This makes it easier to design, deploy, manage, and scale networks.
- Agility and Flexibility
SDN provides agility in network management. Administrators can adjust network resources quickly and dynamically to meet changing needs, without having to physically reconfigure or install hardware.
- Improved Network Performance and Monitoring
SDN allows for more efficient network resource usage and better traffic flow management, which can lead to improved overall network performance. It also enhances network monitoring and analytics capabilities.
- Enhanced Security
By providing centralized control, SDN can improve network visibility and security. Policies can be applied consistently across the network, and security settings can be updated network-wide in real-time.
SDN is widely considered a key component in modern networking, especially useful in environments that require high levels of scalability, flexibility, and manageability, such as cloud computing and data centers.
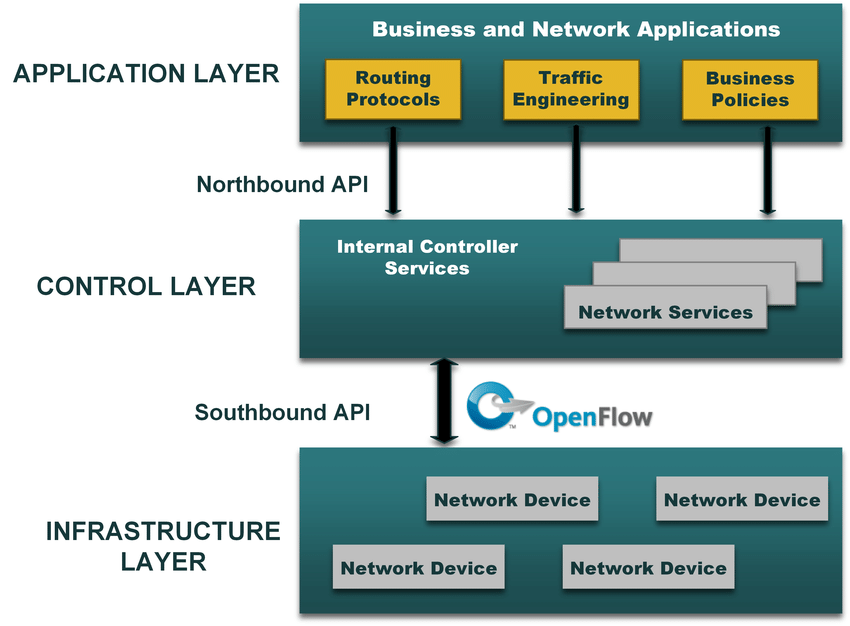
1.2.Software-Defined Networking Security
SDN (Software-Defined Networking) Security refers to the protective measures and protocols put in place to secure the architecture and operations of SDN environments. SDN changes how networks are designed and managed, replacing traditional network hardware with software-based controllers that provide more flexibility and programmability. Key aspects of SDN security include
- Controller Security
Protecting the SDN controller, which is the central point of control in an SDN network.
- Data Plane Security
Ensuring the security of network data paths and flow tables managed by the SDN controllers.
- Network Segmentation
Using SDN’s flexibility to isolate network segments, reducing the spread of cyber threats.
- Policy Enforcement
Implementing consistent and dynamic security policies across the network.
1.3.Threat Intelligence
Threat Intelligence involves collecting, analyzing, and interpreting information about existing or potential cyber threats and attack vectors. It’s a critical aspect of cybersecurity, providing organizations with knowledge that can help them prepare, protect, and identify potential cybersecurity threats. Key elements of threat intelligence include
- Data Collection
Gathering information from various sources such as logs, feeds, and databases.
- Analysis
Interpreting the data to identify patterns, tactics, techniques, and procedures used by cyber attackers.
- Actionable Insights
Providing information that organizations can use to take proactive measures against potential threats.
- Continuous Process
Threat intelligence is ongoing, adapting to new threats as they arise.
1.4.Cloud Computing
Cloud computing involves providing various computing services like servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence through the internet, known as “the cloud”. This approach enhances innovation speed, provides flexible resources, and achieves economies of scale. It enables users to save files and applications on off-site servers and access them over the internet. Its main features are its rapid innovation capabilities, resource flexibility, and scale efficiency.
Users can provide computing resources as needed without requiring human interaction with service providers.
- Widespread Network Accessibility (Broad Network Access)
Services can be accessed via the network using established methods, allowing for compatibility with a variety of platforms.
- Consolidated Resource Utilization (Resource Pooling)
The computing resources of the provider are amalgamated to cater to numerous users, with a dynamic allocation and reallocation of both physical and virtual resources as per user needs.
- Flexible and Scalable Resources (Rapid Elasticity)
The system’s capabilities can be quickly and flexibly scaled up or down, often automatically, to match the fluctuating demands.
- Measured Service
Cloud systems automatically control and optimize resource use by leveraging a metering capability at some level of abstraction appropriate to the type of service.
1.5.Threat Intelligence for SDN Security and its impact on cloud computing
Threat Intelligence for SDN (Software-Defined Networking) Security refers to the application of data analysis to understand and predict cyber threats targeting networks that are managed using SDN. In cloud computing, where SDN is often employed to enhance flexibility and control of network resources, integrating threat intelligence can significantly impact security measures.
1.5.1. Threat Intelligence in SDN Security
Application in SDN
SDN provides a more dynamic and programmable approach to network management compared to traditional networking approaches. In an SDN environment, threat intelligence can be used to quickly adapt network configurations in response to identified threats. For example, it can dynamically alter network paths, implement additional security controls, or isolate parts of the network in response to a detected threat.
1.5.2. Impact on Cloud Computing
- Enhanced Security
Cloud computing environments, which often use SDN for efficient network management, benefit from the integration of threat intelligence. This integration can lead to enhanced detection and response capabilities against cyber-attacks, which is crucial in cloud environments where multiple tenants and vast amounts of data are involved.
- Predictive Analytics
By employing predictive analytics, threat intelligence in SDN environments can forecast potential security incidents, allowing for proactive measures rather than reactive responses.
- Automation and Orchestration
SDN, combined with threat intelligence, allows for more sophisticated automation and orchestration of security responses in the cloud. This can include automatic re-routing of traffic, isolation of compromised network segments, and the deployment of specific security resources where needed.
- Customization and Scalability
The flexibility of SDN allows cloud service providers to customize security measures for different clients or services. Additionally, threat intelligence can be scaled as per the size and complexity of the cloud environment, providing tailored security postures.
- Reduced Latency
Integrating threat intelligence within SDN can reduce the time taken to detect and respond to security threats, which is essential for maintaining service continuity in cloud services.
- Cost Efficiency
Improved security efficiency can lead to cost savings for cloud providers and users, as threat intelligence helps in avoiding expensive data breaches and ensuring regulatory compliance.
- Challenges and Considerations
While beneficial, the integration of threat intelligence in SDN within cloud computing also presents challenges such as data privacy concerns, the need for continuous updates of threat databases, and ensuring that automated responses do not disrupt legitimate network activities.
In summary, Threat Intelligence for SDN Security plays a critical role in enhancing the overall security posture of cloud computing environments. It brings in proactive, predictive, and automated approaches to network security, aligning with the dynamic and scalable nature of cloud services.
Threat intelligence is crucial for identifying potential security threats, SDN security focuses on protecting the flexible and programmatically managed network architectures, and cloud computing represents the on-demand provision of computing resources over the internet.
Top of Form
Bottom of Form
02.Literature review
2.1. Historical Evolution of Threat Intelligence in SDN
“Cyberthreat Intelligence: Challenges and Opportunities” by Mauro Conti, Ali Dehghantanha, Tooska Dargahi [1]
- This paper discusses the evolution of cyberthreats and the corresponding development of threat intelligence. It emphasizes the role of artificial intelligence and machine learning in evolving threat intelligence, especially in the context of Software-Defined Networking (SDN), Internet of Things (IoT), and cloud computing. The authors detail the lifecycle of cyber-attacks and the challenges in recognizing attack vectors and indicators, necessitating advanced cyberthreat intelligence methods. [1]
- Methodology The paper reviews the evolution of cyber threats and the corresponding development of threat intelligence, focusing on how AI, machine learning, and data mining techniques have been used.
- Results and Drawbacks It emphasizes the increasing complexity of cyber-attacks, necessitating advanced analytical techniques, but also highlights challenges such as the need for real-time response and the identification of attack points. [1]
2.2. Theoretical Frameworks and Models in SDN-Based Threat Intelligence
“Threat Intelligence and Machine Learning for Cloud Security: Enhancing Detection and Response” by Asaad Abbas [2]
- The paper explores various techniques for protecting virtual machines (VMs) in cloud environments, focusing on hypervisor security and isolation methods. It highlights the application of hardware-assisted virtualization, secure boot processes, virtual machine introspection, and software-defined networking (SDN) as key to enhancing cloud security and VM protection.
- Methodology This study focuses on the security of VMs in cloud environments, exploring hypervisor security and isolation techniques.
- Results and Drawbacks The paper concludes that implementing robust VM security measures, including hardware-assisted virtualization and SDN for VM isolation, is essential for cloud security. It acknowledges the challenges posed by shared cloud resources. [2]
2.3. Case Studies on Threat Intelligence Implementation in SDN
“Using Cyber Threat Intelligence to Prevent Malicious Known Traffic in a SDN Physical Testbed” by Jorge Buzzio García, Víctor Salazar Vilchez, Jeffrey Zavala Castro, Jose L. Quiroz Arroyo [3]
- This study presents a case of using cyber incident reports obtained through Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI) in a Software-Defined Network (SDN) testbed. The research illustrates how incident reports are translated into OpenFlow flow entries to prevent known attacks in an SDN environment, demonstrating practical implementation and results of CTI in SDN [3]
- Methodology Implementation of Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI) in a real-hardware SDN testbed using Python, focusing on how CTI can be used to improve network security and block malicious traffic.
- Results and Drawbacks Demonstrates successful prevention of malicious traffic through CTI integration in SDN, but notes that the limited number of ports on OpenFlow switches can be a constraint in a production. [3]
2.4. Technologies and Tools in SDN for Threat Intelligence
Network Security and Management in SDN by Zhiping Cai,1ChengchenHu,2 KaiZheng,3 YangXu,4 andQiangFu5. [4]
- This paper discusses the challenges and innovations in network security and management in Software Defined Networking (SDN). The authors propose solutions like a cross-plane distributed DoS attack defense framework, collaborative intelligence between data plane and control plane, and algorithms for attack classification and detection. The vulnerability of SDN due to the separation of control and data planes is highlighted, with emphasis on mitigating risks through diverse defense mechanisms. [4]
- Methodology This study proposes various security mechanisms for SDNs, such as a cross-plane distributed DoS attack defense framework, a game-theoretic model for analyzing security performance, and an FPGA-based mechanism for accelerating and securing SDN switches. [4]
- Results and Drawbacks The proposed methods include collaborative DDoS attack detection, lightweight DoS detection systems, and intrusion-tolerant systems. The drawbacks include potential performance bottlenecks and complexity in the implementation of these advanced security technologies. [4]
2.5. Methodologies for Threat Detection and Response in SDN
Is SDN the Real Solution to Security Threats in Networks? A Security Update on Various SDN Models by Naveen Bindra and Manu Sood. [5]
- Methodology This paper evaluates existing significant security mechanisms in SDNs and proposes a secure architecture for new generation networking. It covers various threat mitigation mechanisms such as automatic trust solutions, replication of controllers, credential verification, and moving target defense. Also, the paper evaluates various SDN models to understand their effectiveness in mitigating security threats in networks. The authors analyze these models based on criteria like area of focus, mitigation solutions, and drawbacks. [5]
- Results and Drawbacks The study concludes that no single SDN model can address all prevalent security issues, suggesting the need for a generalized, inclusive SDN architecture. The proposed model aims to incorporate proactive threat detection, adaptive threat mitigation strategies, and resilient services. However, the paper’s main limitation is its theoretical approach, lacking practical demonstrations or empirical evidence to support the proposed model’s efficacy in real-world scenarios. [5]
2.6. Integration Challenges and Solutions
Research on Cloud Computing Network Architecture Based on SDN Technology by Weibo Li [6]
- Weibo Li explores how Software Defined Networking (SDN) can address the evolving needs of cloud computing networks. The paper proposes using Overlay SDN technology to solve issues like network flow control, address management, and security control in cloud environments. The proposed architecture combines SDN and Overlay network virtualization to enhance function flexibility and communication performance in cloud computing. [6]
- Methodology This paper analyzes the integration of SDN technology into cloud computing networks to address challenges such as network flow control, address reuse, access control, security control, and automatic network configuration.
- Results and Drawbacks The study suggests that Overlay SDN technology effectively resolves the complexities of traditional cloud networks and enhances automatic connection performance. It notes, however, that the integration of SDN into cloud computing networks is challenging due to the need to manage the scalability and dynamic nature of cloud services. [6]
2.7. Performance Metrics and Evaluation of SDN-Based Threat Intelligence Systems.
Survey on SDN Security Mechanisms by Teenu Jose and Jincy Kurian [7]
- This survey paper by Jose and Kurian provides an in-depth analysis of SDN’s architecture and its impact on security. It categorizes SDN attacks and explores various security mechanisms. Key focus areas include the vulnerabilities due to centralized control and network programmability, DDoS attacks on different layers of SDN, and security solutions like FRESCO, STRIDE, and Ethane. The paper also emphasizes the need for dynamic security mechanisms in SDN environments. [7]
- Methodology This survey discusses various SDN security mechanisms and their role in protecting networks against diverse threats, including DDoS attacks and control plane vulnerabilities.
- Results and Drawbacks The paper identifies key SDN security mechanisms and highlights the importance of performance metrics in evaluating the effectiveness of these systems. It points out the need for comprehensive security strategies that cover all layers of the SDN architecture, from data planes to controllers. However, it also indicates that developing such comprehensive security solutions is complex and challenging due to the dynamic and diverse nature of threats in SDN environments. [7]
2.8.Impact of SDN-Based Threat Intelligence on Cloud Security
Cloud Computing Security for Multi-Cloud Service Providers: Controls and Techniques in our Modern Threat Landscape by Sandesh Achar [8]
- Achar’s paper covers a broad range of security concerns for organizations using cloud services, specifically focusing on multi-cloud environments. It discusses the implementation of identity and access management, data encryption, egress and ingress traffic control, vulnerability and threat management, and auditing. The paper provides insights into the complexity of cloud computing security and offers solutions to address these challenges. [8]
- Methodology The paper explores various aspects of cloud security, including identity and access management, data encryption, and traffic control, and provides recommendations for multi-cloud service providers.
- Results and Drawbacks It stresses the importance of robust security measures, such as IAM and data encryption, in ensuring cloud data safety. The paper acknowledges the challenges inherent in securing a multi-cloud environment and offers solutions to overcome these challenges. However, it also notes the constant evolution of cyber threats, necessitating ongoing updates and improvements in security measures for cloud computing environments. [8]
2.9. Future Trends and Emerging Research in SDN and Threat Intelligence.
A study on the Computing Framework of Cloud Intelligence Business Platforms by Feiqi Wang and Jian Zhang. [9]
- This paper discusses the integration of Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA) and cloud computing for business platforms, emphasizing hierarchical design and virtualization technology to enhance business hardware resources in cloud environments. [9]
- Methodology This study focuses on the integration of Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA) and cloud computing for business platforms. It emphasizes the importance of hierarchical design and virtualization technology to enhance the flexibility and efficiency of business hardware resources in cloud environments. [9]
- Results and Drawbacks The paper proposes an effective solution for managing diverse business applications and systems through cloud intelligence platforms. However, the study primarily focuses on the theoretical aspects and lacks empirical validation or case studies to demonstrate the practical implementation of the proposed framework. [9]
The survey on “Threat Intelligence in Software-Defined Networking for Cloud Computing” has provided extensive insights into how threat intelligence, when integrated with SDN, profoundly impacts cloud computing security. It demonstrates that the foundational principles of SDN in cloud environments, primarily its early concepts and core architectural elements, have set the stage for more secure and efficient cloud computing paradigms.
Threat intelligence plays a pivotal role in cloud security. Its scope and definition within the cybersecurity domain have been clearly established, underscoring its significance in safeguarding cloud environments [10]. By integrating threat intelligence into SDN, we see enhanced cloud security through innovative strategies and methodologies, as evidenced by various case studies. These integrations have successfully tackled numerous cyber threats, highlighting the dynamic nature of this field.
The tools and technologies developed for SDN-based threat intelligence have shown considerable promise. Their efficiency and scalability, as demonstrated in comparative analyses, illustrate their potential in improving cloud security. Methodologically, the approaches for threat detection and prevention in SDN-enabled cloud systems have proven effective, although there are challenges and limitations in their implementation. The survey underscores these challenges, particularly in the integration of threat intelligence in SDN for cloud computing and discusses potential solutions and mitigation strategies.
Real-world applications and case studies presented in the survey reflect the direct impacts of integrating threat intelligence on cloud computing security and performance. They demonstrate improved security postures and reveal potential trade-offs, providing valuable lessons and success stories.
Looking towards future trends, the survey predicts further advancements in SDN and cloud security, indicating emerging technologies that could significantly influence these fields. It also identifies critical gaps in current research, providing a roadmap for future investigations.
In summary, the integration of threat intelligence in SDN has emerged as a vital factor in enhancing cloud computing security. It brings a proactive, predictive, and automated approach to network security, aligning with the dynamic and scalable nature of cloud services. While challenges persist, ongoing research and development in this domain continue to push the boundaries, promising even more robust and efficient cloud computing environments in the future.
03. How The Threat Intelligence for SDN Security Impacted for Cloud Computing.
3.1. Foundations of Software-Defined Networking (SDN) in Cloud Computing
SDN has revolutionized cloud computing with its early concepts and core principles, providing a platform for enhanced flexibility, programmability, and centralized control. The decoupling of control and data planes has facilitated a more agile and efficient management of network resources, proving essential in modern cloud environments.
3.2. Role and Importance of Threat Intelligence in Cloud Security
The role of threat intelligence in cloud security is indispensable. Its scope extends to collecting and analyzing data to predict and respond to cyber threats, thereby playing a crucial role in securing cloud environments. The integration of threat intelligence is vital for proactive cybersecurity measures in the cloud.
3.3. Integrating Threat Intelligence into SDN for Enhanced Cloud Security
Integrating threat intelligence into SDN has shown significant improvements in cloud security. Strategies and methodologies developed for this integration have successfully addressed specific security challenges in cloud environments, as demonstrated by various case studies.
3.4. Tools and Technologies in SDN-Based Threat Intelligence for Cloud Security
The survey reveals a wide array of tools and technologies designed for SDN-based threat intelligence. These tools have been critically analyzed for their efficiency and scalability, demonstrating their capability to enhance security in cloud computing environments.
3.5. Methodological Approaches to Threat Detection and Prevention in SDN-Enabled Cloud Systems
Various methodologies for threat detection and prevention in SDN-enabled cloud systems have been explored. These methods are effective in enhancing cloud security, showcasing the adaptive nature of SDN in responding to evolving cyber threats.
3.6. Challenges and Limitations in Implementing Threat Intelligence in SDN for Cloud Computing
The implementation of threat intelligence in SDN for cloud computing faces challenges and limitations, including scalability issues, data privacy concerns, and the need for continuous updates. The survey discusses these challenges along with potential solutions and mitigation strategies.
3.7. Case Studies and Real-World Applications
Real-world applications and case studies have demonstrated the practical effectiveness of integrating threat intelligence in SDN for cloud computing. These studies provide insights into successful implementations and the lessons learned, highlighting the real impact on cloud security.
3.8. Impact of Threat Intelligence on Cloud Computing Security and Performance
The integration of threat intelligence in SDN has a profound impact on the security and performance of cloud computing. It enhances security postures and reduces latency, thereby improving the overall effectiveness of cloud services.
3.9. Emerging Trends and Future Directions in SDN and Cloud Security
The survey predicts future trends in SDN and cloud security, indicating that emerging technologies will continue to shape these domains. It underscores the dynamic nature of these fields and the importance of staying abreast of technological advancements.
3.10. Critical Analysis and Synthesis of Reviewed Literature
A critical analysis and synthesis of the literature reviewed in this survey reveal key findings and identify gaps in current research. These insights pave the way for future investigations and highlight areas requiring further exploration to enhance threat intelligence in SDN for cloud computing.
In conclusion, this survey underscores the significant impact of integrating threat intelligence into SDN for cloud computing. It highlights the evolution, current state, and future prospects of this integration, emphasizing its role in enhancing cloud security and addressing the dynamic nature of cyber threats.
04. Conclusion
In conclusion, the survey “Threat Intelligence in Software-Defined Networking for Cloud Computing: A Survey” has thoroughly explored the integration of Threat Intelligence in Software-Defined Networking (SDN) and its significant impact on cloud computing. Through various research papers studied between 2020 and 2024, it becomes evident that the incorporation of threat intelligence into SDN has markedly enhanced the security landscape of cloud computing environments.
The historical evolution of threat intelligence in SDN, as discussed in the works of Mauro Conti, Ali Dehghantanha, and Tooska Dargahi, highlights the increasing complexity of cyber-attacks and the crucial role of AI and machine learning in developing advanced cyberthreat intelligence [1]. This advancement is pivotal in addressing the challenges posed by evolving attack vectors, especially in the dynamic and scalable cloud environments.
Theoretical frameworks and models, such as those explored by Asaad Abbas, have demonstrated how SDN can fortify cloud security through techniques like hardware-assisted virtualization and secure boot processes [2]. The application of these models in real-world scenarios, such as the physical testbed validates the effectiveness of integrating threat intelligence in SDN, albeit with considerations like the limitations of hardware resources [3].
Technological advancements in SDN, discussed by authors like Zhiping Cai,1ChengchenHu,2 KaiZheng,3 YangXu,4 andQiangFu5, present a comprehensive approach towards mitigating diverse threats, including DDoS attacks and control plane vulnerabilities. [4]. These advancements underscore the importance of dynamic and multi-layered security mechanisms that are responsive to the continually evolving threat landscape in cloud computing.
The integration of threat intelligence into SDN has also led to notable improvements in performance metrics and evaluation systems, as surveyed by Teenu Jose and Jincy Kurian [7]. Such evaluations are crucial in understanding the effectiveness of SDN security mechanisms and ensuring that they can dynamically adapt to new threats.
Looking forward, the insights gathered from various studies indicate a future where threat intelligence in SDN will continue to evolve and play a critical role in cloud computing. The continuous development of predictive analytics, automation, orchestration, and customization in SDN security promises to enhance the resilience of cloud environments against sophisticated cyber threats. As cloud technology advances, ongoing research and the adoption of robust security measures are imperative to address emerging threats and uphold the highest standards of cloud security.
In essence, the survey has shed light on the critical importance of integrating threat intelligence in SDN for cloud computing, highlighting its impact on enhancing security, predictive capabilities, and overall network resilience. This integration not only addresses current security challenges but also paves the way for future developments in the field, ensuring the security and reliability of cloud services in an ever-evolving digital landscape.
Top of Form
Bibliography
| [1] | A. D. a. T. D. Mauro Conti, “Cyberthreat Intelligence:Challenges and Opportunities,” p. 05, 03 Aug 2020 [Online]. Available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1808.01162[Accessed:11-Mar-2024] doi: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1808.01162. |
| [2] | A. A. S. Luqman, “Threat Intelligence and Machine Learning for Cloud Security:Enhancing Detection and Response,” p. 08, 03 July 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/372448942 [Accessed:12-Mar-2024] |
| [3] | V. S. V. J. Z. C. J. L. Q. A. Jorge Buzzio García, “Using Cyber Threat Intelligence to Prevent Malicious Known Traffic in a SDN Physical Testbed,” p. 04, 14 Aug 2020. [Online]. Available: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8853616 [Accessed:11-Mar-2024]doi: 10.1109/INTERCON.2019.8853616 |
| [4] | 1. C. K. Y. a. Zhiping Cai, “Network Security and Management in SDN,” p. 03, 04 June 2021. [Online]. Available:https://www.hindawi.com/journals/scn/2018/7928503/ [Accessed:15-Mar-2024] doi: https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/7928503 |
| [5] | N. B. a. M. Sood, “Is SDN the Real Solution to Security Threats in Networks? A Security Update on Various SDN Models,” vol. 09, no. 32, p. 08, 16 Aug 2022. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/308043223_Is_SDN_the_Real_Solution_to_Security_Threats_in_Networks_A_Security_Update_on_Various_SDN_Models [Accessed:13-Mar-2024]doi: 10.17485/ijst/2016/v9i32/100214 |
| [6] | W. Li, “SDN, Research on Cloud Computing Network Architecture Based on SDN Technology,” p. 06, January 2020. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/315562543_Research_on_Cloud_Computing_Network_Architecture_Based_on_SDN_Technology [Accessed:20-Mar-2024] doi: 10.2991/icmmct-16.2016.237 |
| [7] | T. J. J. Kurian, “Survey on SDN Security Mechanisms,” vol. 132, no. 14, p. 04, 21 Dec 2022. [Online]. Available: https://www.academia.edu/90354179/Survey_on_SDN_Security_Mechanisms?uc-sb-sw=37033242 [Accessed:15-Mar-2024] doi: 10.2991/icmmct-16.2016.237 |
| [8] | S. Achar, “Cloud Computing Security for Multi-Cloud Service Providers: Controls and Techniques in our Modern Threat Landscape,” vol. 16, no. 08, p. 06, 20 May 2022. [Online]. Available: https://www.academia.edu/90477930/Cloud_Computing_Security_for_Multi_Cloud_Service_Providers_Controls_and_Techniques_in_our_Modern_Threat_Landscape [Accessed:15-Mar-2024] |
| [9] | J. Z. Feiqi Wang, “A study on the Computing Framework of Cloud Intelligence Business Platforms,” Advances in Engineering Research, vol. 149, p. 07, 15 Mar 2023. [Online]. Available: A study on the Computing Framework of Cloud Intelligence Business Platforms.pdf[Accessed:18-Mar-2024] |
| [10] | D. A. d. S. R. T. d. S. J. u. Wanderson Paim de Jesus, “Analysis of SDN Contributions for Cloud Computing Security,” p. 07, 20 Sept 2021. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/271850329 [Accessed:18-Mar-2024]doi: 10.1109/UCC.2014.150 |

Leave a comment